- About Us
- Services
- Endodontics
- Root Canal Treatment
- Post & Core
- Single Visit RCT
- Apicoectomy
- Re-RCT
- Restorations
- Composite Restorations
- Laminates & Veneers
- Inlays & Onlays
- Dental Implants Crowns & Bridges
- Dental Implants
- PFM & All Ceramic Crowns & Bridges
- Complete Dentures
- Othodontics
- Metallic & Ceramic Braces
- Lingual Braces
- Invisalign (Invisible Braces)
- Periodontics
- Ultrasonic Scaling
- Gums Depigrnentation
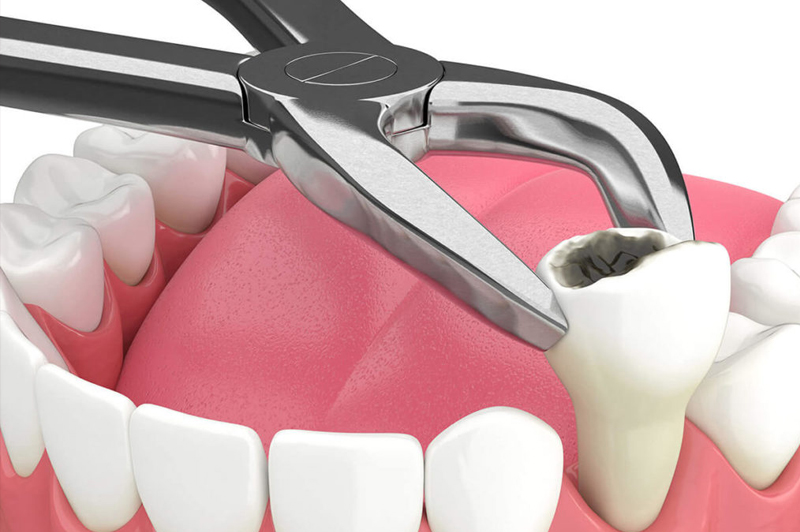
- Oral Surgery
- Extractions
- Impacted Teeth Removal
- Miscellaneous
- Dental Lasers
- Dental Bleaching
- Cases
- Contact Us